Scoliosis Treatment: Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, often diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. This condition can lead to various physical challenges, pain, and emotional distress for the affected individuals. As experts in foot care, our mission is to provide extensive information and resources for understanding and treating scoliosis effectively.
Understanding Scoliosis
Scoliosis affects approximately 3% of the population, making it a common condition that can have significant long-term impacts. There are several forms of scoliosis, including:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis: The most prevalent form, often developing in adolescents with no known cause.
- Congenital Scoliosis: Present at birth due to malformation of the spine.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Resulting from conditions affecting the muscles and nerves, such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
Recognizing the type of scoliosis is crucial for determining the appropriate scoliosis treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of scoliosis can vary depending on the degree of curvature and its progression. Common signs include:
- Visible Curvature of the Spine: A noticeable S or C shape when viewed from the back.
- Uneven Shoulders or Hips: One shoulder may be higher than the other, or hips may appear uneven.
- Back Pain: Discomfort that may worsen over time, especially in adults.
- Fatigue: Increased tiredness due to muscle strain from maintaining balance.
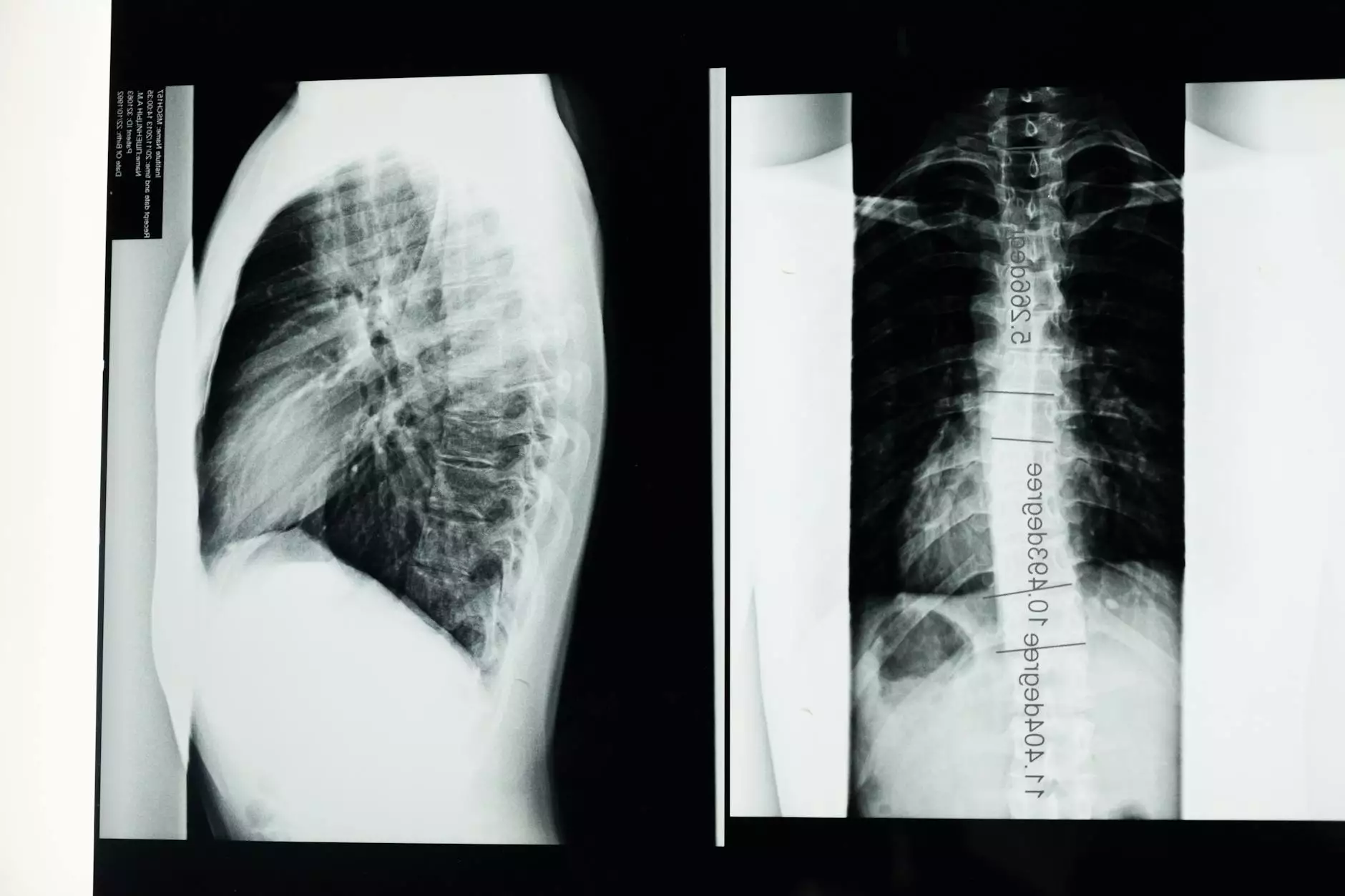
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs. A healthcare professional will measure the angle of curvature, known as the Cobb angle, to assess the severity of scoliosis.
Effective Scoliosis Treatment Options
The choice of scoliosis treatment largely depends on the severity of the curve, the age of the patient, and the potential for progression. Treatment options include:
Observation
In cases where the curvature is mild (less than 20 degrees) and not expected to worsen, a physician may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor any changes in the curvature.
Bracing
For adolescents whose bones are still growing and have scoliosis between 20 and 40 degrees, a brace may be prescribed. Bracing aims to prevent further curvature and is most effective during the growth spurts.
It's important to note that while bracing does not correct existing curves, it can effectively halt progression in many cases.
Surgery
When scoliosis is severe (greater than 40 degrees) or is progressing rapidly, surgical intervention may be necessary. The most common surgical procedure is spinal fusion, which involves connecting two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
Surgeons may also use rods, screws, or hooks to straighten the spine during this procedure. Modern surgical techniques have improved safety, effectiveness, and recovery times, making this a viable option for many patients.
Complementary Treatments and Support
In addition to primary treatments, many individuals find relief through complementary approaches:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can help strengthen core muscles, improve posture, and alleviate back pain.
- Chiropractic Care: Although chiropractors cannot treat scoliosis, they can offer relief for muscle tension and discomfort associated with scoliosis.
- Yoga and Pilates: Mind-body practices focus on flexibility, strength, and overall well-being, benefiting those with scoliosis.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help relax tense muscles and provide temporary relief.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any complementary treatments.
Living with Scoliosis
Living with scoliosis requires adaptation. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Maintain Good Posture: Focus on keeping a balanced position when sitting, standing, or walking to minimize strain.
- Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical activity tailored to your abilities supports overall health and can reduce discomfort.
- Seek Support: Connecting with support groups or counseling can aid in managing the emotional aspects of the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes scoliosis?
The precise cause of idiopathic scoliosis remains unknown. Genetic factors, growth patterns, and environmental factors may all contribute to its development. Congenital and neuromuscular scoliosis have identifiable causes related to vertebral development or muscle dysfunction.
At what age is scoliosis usually diagnosed?
Scoliosis commonly manifests between the ages of 10 and 15, coinciding with rapid growth periods. Regular screenings in schools help identify at-risk individuals early.
Can scoliosis be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent scoliosis, early detection and treatment can significantly reduce its severity and associated complications.
Can adults develop scoliosis?
Yes, adults can develop scoliosis, often due to aging, degeneration of spinal discs, or previous untreated adolescent scoliosis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing scoliosis is essential for leading a fulfilling life. From early diagnosis to effective treatment options like bracing and surgery, individuals can mitigate the impacts of this condition. Integrating complementary therapies and maintaining a supportive lifestyle can further promote overall well-being.
If you or someone you know is seeking scoliosis treatment, consult with a healthcare professional to explore personalized options that best suit your needs.
For more information on foot care and general health practices, visit The Foot Practice.









