The Anatomy of a Car Braking System
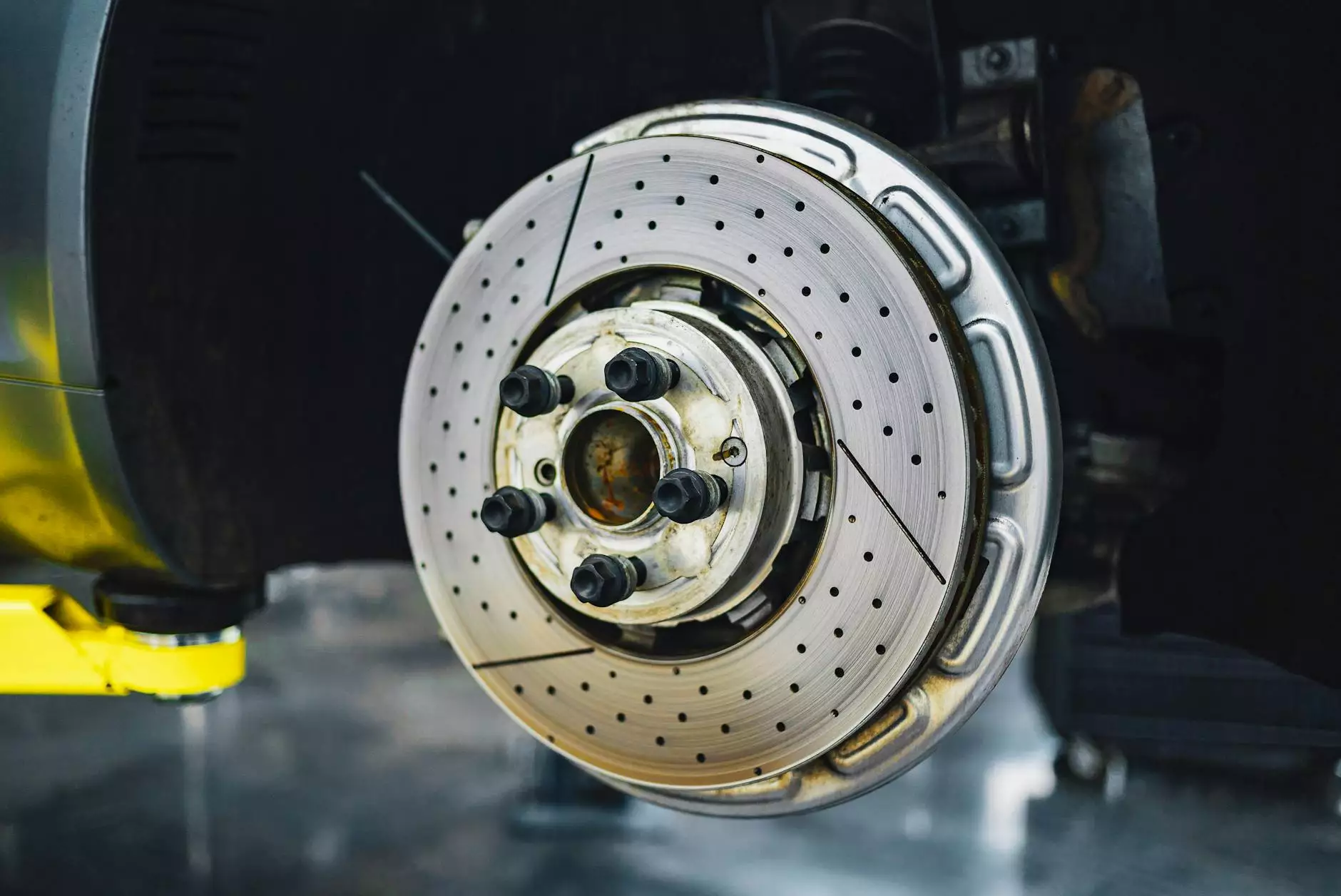

When it comes to the safety and performance of a vehicle, one of the most critical systems that deserve attention is the braking system. A car's braking system is a complex network of components working together seamlessly to provide safe and reliable stopping power. Understanding the various parts of a car braking system is essential for every car owner to ensure optimal functionality and safety on the road.
Brake Pads
Brake pads are one of the key components of a car's braking system that directly interact with the brake rotors to create friction and slow down or stop the vehicle. These pads are typically made of high-friction materials that wear down over time and need to be replaced periodically to maintain braking efficiency.
Brake Rotors
Brake rotors, also known as brake discs, are flat, round metal discs that spin with the wheel and are squeezed by the brake pads to create friction and stop the vehicle. It is crucial to have properly functioning brake rotors to ensure smooth and effective braking performance.
Calipers
The calipers are responsible for holding the brake pads in place and pressing them against the brake rotors when the brake pedal is engaged. These components play a critical role in the braking process, as they control the amount of pressure exerted on the brake pads to stop the vehicle efficiently.
Brake Lines
Brake lines are the tubes that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers. They are crucial for transmitting hydraulic pressure to the braking system components, enabling smooth and responsive braking. It is essential to regularly inspect brake lines for signs of wear or leaks to prevent brake system failure.
Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is a vital component that converts mechanical force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is then transmitted through the brake lines to the calipers. A properly functioning master cylinder is essential for maintaining proper brake fluid pressure and ensuring reliable braking performance.
Brake Fluid
Brake fluid is a hydraulic fluid that plays a crucial role in transmitting force within the braking system. It is important to have the right type of brake fluid and maintain proper fluid levels to ensure optimal brake performance. Contaminated or low brake fluid can lead to reduced braking effectiveness and potential safety hazards.
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
The anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety feature that prevents wheel lock-up during sudden braking or slippery road conditions. ABS helps maintain steering control and stability by modulating brake pressure to individual wheels, allowing the driver to retain control of the vehicle during emergency braking situations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the braking system of a car is a sophisticated network of components that work together to ensure safe and reliable stopping power. Understanding the intricate parts of a car braking system, such as brake pads, rotors, calipers, brake lines, master cylinder, brake fluid, and ABS, is vital for maintaining optimal performance and safety on the road. By paying attention to these components and performing regular maintenance, car owners can enjoy peace of mind knowing that their vehicle's braking system is in top condition.